A risk factor is something that raises a person’s risk of developing an illness like cancer. Different malignancies have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be adjusted, while others, such as a person’s age or family history, are unchangeable.
However, risk variables do not tell us everything because the presence of one or two risk factors does not guarantee that a person will develop the disease. Many of those who get the disease have few or no identified risk factors.
What are the Risk Factors for Tongue Cancer?
The following are a few of the risk factors associated with tongue cancer:
Tobacco and alcohol abuse: Tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption are two of the most common causes of oral cancer. People who consume large amounts of alcohol and smoke have a 30 times greater risk of developing tongue cancer than those who do not.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the most common sexually transmitted infection, and HPV16 is often linked to oropharyngeal cancers, particularly those in the tonsils and at the base of the tongue.
Gender: Men are twice as likely as women to have oral and oropharyngeal cancers.
Age: Cancers of the oral cavity and oropharynx usually take many years to develop, so they are less common among young people. Oral cancer is most commonly observed in people aged 55 or older.
Genetic conditions: Certain genetic conditions have a very high risk of developing mouth and throat cancer.
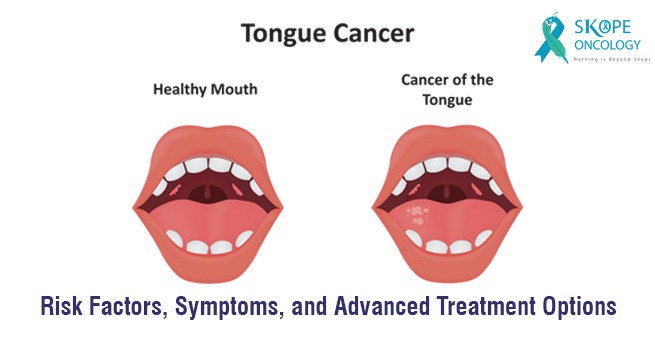
What are the symptoms of Tongue Cancer?
The symptoms of tongue cancer may include:
- Persistent red or white patches on the tongue
- Persistent numbness and soreness in the mouth and throat
- Pain during swallowing
- Burning sensation of the tongue
- A lump in the neck
- Unexplained bleeding from the tongue
It is important to keep in mind that these symptoms could indicate a less serious medical problem. However, it is always recommended to get your symptoms checked by a doctor.
Can Tongue Cancer be Treated?
Surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, in combination or alone, are the main treatments for tongue cancer. The treatment will be determined by the size and stage of the tumor. It also depends on the location of the tongue that is affected.
Surgery
Depending on the size of the tumor, the doctor may perform primary tumor resection (removing the tumor and an area of normal tissue around it) or glossectomy (removing a part or all of the tongue), followed by tongue reconstruction. To lower the risk of cancer recurrence, a neck dissection may be performed to remove the lymph nodes from one or both sides of your neck.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy destroys cancer cells by using high-energy waves similar to X-rays. It may be given on its own or combined with chemotherapy and surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells by using cytotoxic (anti-cancer) drugs. The most commonly used drugs are cisplatin, fluorouracil (5FU), and carboplatin.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment in which medications are used to target certain genes and proteins in cancer cells that help them survive and proliferate.
They may include monoclonal antibodies such as Cetuximab and immunotherapeutic medicines such as Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab.
Early detection of cancer often results in improved treatment outcomes and lower morbidity and mortality. Though it is not possible to prevent the occurrence of tongue cancer, it is recommended to consult an oncologist if you notice any of the signs or symptoms of tongue cancer.