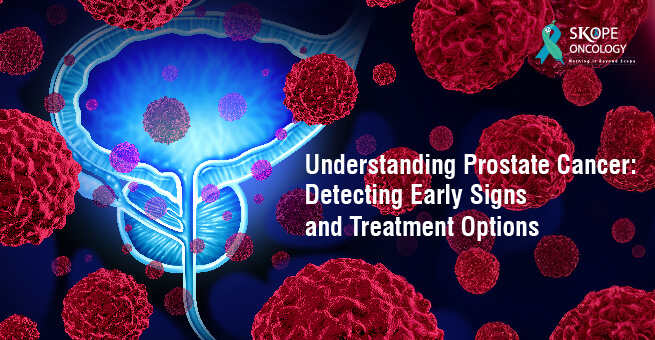
Prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers among men, affecting the walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder. While it may sound alarming, understanding the early signs and available treatment options can make a significant difference in managing this condition.
What is Prostate Cancer?
The prostate, part of the male reproductive system, plays a crucial role in producing semen. When cells in the prostate gland begin to grow uncontrollably, it leads to prostate cancer. Age, family history, and ethnicity are among the factors that might increase the risk.
Signs and symptoms
Recognizing the signs early can greatly impact the outcome. Hence it is crucial to kKeep an eye out for difficulties in urination, blood in urine or semen, or persistent pain in the back, hips, or pelvis. However, in its early stages, prostate cancer might not exhibit any symptoms, which makes regular screenings crucial.
Early Detection Methods
Screening for prostate cancer typically involves a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam. The PSA test measures the levels of prostate-specific antigen in the blood, while the rectal exam allows the doctor to physically assess the prostate for abnormalities. These tests can detect potential issues early, offering a better chance at successful treatment.
Understanding Diagnosis
If these tests show any abnormalities, further tests, like biopsies, will be conducted for confirmation. A biopsy is the removal of a small sample of prostate tissue for microscopic examination. While the process might seem intimidating, it’s pivotal in determining the presence of cancerous cells.
Treatment Options
Active Surveillance
For cases where the cancer is slow-growing and less aggressive, active surveillance might be recommended with regular check-ups and monitoring the cancer’s progression to determine if treatment becomes necessary.
Surgery
Surgery, known as a radical prostatectomy, involves removing the prostate gland. It’s a common treatment, especially for localised cancer. While it’s effective, there might be side effects like urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction, which can improve with time and therapy.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, using high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells, can be delivered externally or through implanted radioactive seeds (brachytherapy). It’s a non-invasive option that offers promising results, though it may cause side effects like fatigue or urinary problems.
Hormone Therapy
In some cases, hormone therapy is used to slow cancer growth by reducing testosterone levels. While effective, it might lead to side effects such as hot flashes and loss of libido.
Lifestyle and Supportive Care
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet is crucial in managing prostate cancer. Additionally, seeking support from counsellors or support groups can greatly aid in coping with the emotional aspects of the diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Early detection through regular screenings and understanding available treatment options significantly improves the chances of successful prostate cancer management. Remember, consulting healthcare professionals and staying informed about one’s health are key to navigating this journey.
References:
- Prostate Cancer – Early-Stage
https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/prostate-cancer
- What Is Prostate Cancer?
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/what-is-prostate-cancer.html
- Basic Information About Prostate Cancer
https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/basic_info/index.htm
- Prostate Cancer Treatment
https://www.cancer.gov/types/prostate/patient/prostate-treatment-pdq
- Prostate cancer
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-cancer/
- Prostate cancer
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/prostate-cancer