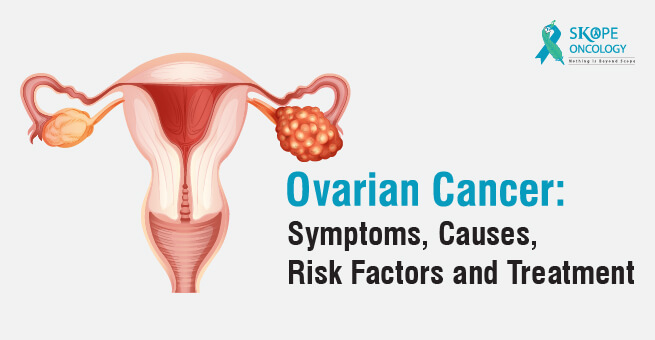
Ovarian cancer is a serious deadly disease that affects thousands of women around the world each year. Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the ovaries, the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and hormones. This type of cancer occurs when cells in the ovaries begin to grow and divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumours.
Ovarian cancer is particularly dangerous because it often goes undetected until it has already spread to other parts of the body. Despite ongoing research efforts, there is still much that is not known about ovarian cancer, including its causes and how to effectively treat it. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes and what women can do to reduce their risk of developing this cancer.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer
In the early stages, ovarian cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms, or the symptoms may be mild and easily confused with other conditions. However, as the cancer grows and spreads, women may experience the following symptoms:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling: Women with ovarian cancer may experience persistent bloating or swelling in the abdomen that does not go away with diet or exercise.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort: Women with ovarian cancer may experience persistent pelvic pain or discomfort, which may feel like a dull ache or a sharp pain.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly: Women with ovarian cancer may have a reduced appetite or feel full more quickly than usual.
- Changes in bowel habits: Women with ovarian cancer may experience changes in their bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhoea.
Frequent urination: Women with ovarian cancer may need to urinate more frequently than usual or have a sudden urge to urinate.
Causes and risk factors of ovarian cancer
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown, but there are several factors that can increase a woman’s risk of developing the disease. These include:
- Age: The risk of ovarian cancer increases as a woman gets older, with most cases occurring in women over 50 years of age.
- Family history: Women who have a first-degree relative (such as a mother, sister, or daughter) who has had ovarian cancer have an increased risk of developing the disease.
- Inherited gene mutations: Certain inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Personal history of breast cancer: Women who have had breast cancer may have an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Hormone therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or fertility drugs may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Endometriosis: Women who have endometriosis (a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it) may have an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
- Reproductive history: Women who have never had children or who had their first child after the age of 35 may have a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
- Obesity: Women who are overweight or obese may have an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer.
It is important to note that having one or more risk factors does not mean that a woman will definitely develop ovarian cancer, and many women with ovarian cancer have no known risk factors. However, if you have any of these risk factors, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider and consider screening and preventive measures.
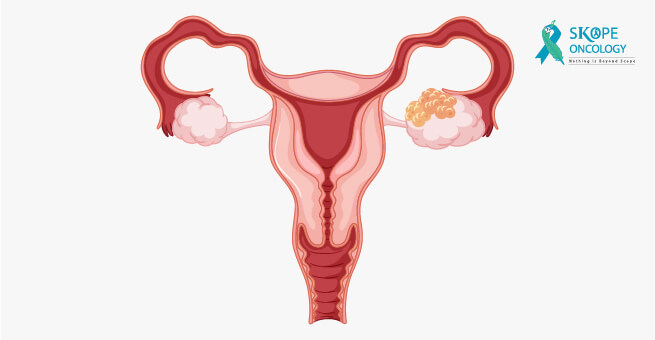
Prevention of ovarian cancer
While there is no surefire way to prevent ovarian cancer, there are steps women can take to reduce their risk of developing the disease. Here are some ways to potentially lower your risk of ovarian cancer:
- Birth control pills: Taking birth control pills for five years or more can lower the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Women who have been pregnant and breastfed their babies have a reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
- Tubal ligation or hysterectomy: Surgical procedures such as tubal ligation (tying the tubes) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Healthy diet and exercise: Eating a healthy diet and regular exercise can help in preventing any cancer at bay.
Ovarian cancer is a condition that might have an adverse effect on a person’s life for a long time. We must never stop informing ourselves and others on the dangers, signs, and accessible treatments. Also, we must keep up our support for those who are battling this illness. We can defeat ovarian cancer and work towards a better future for all by teaming together as a community.