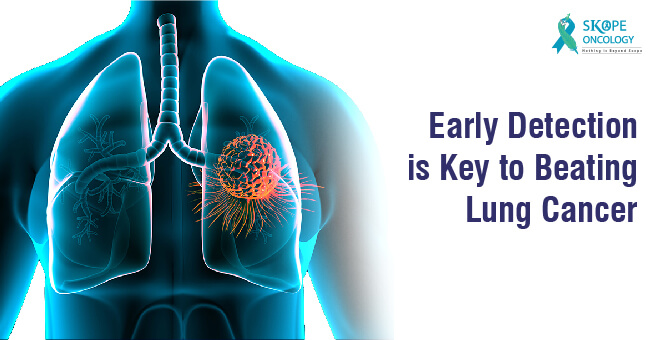
One of the most common myths about any type of cancer is that it will show symptoms in its early stages. According to a recent hospital-based study from northern India, 90% of lung cancer patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage of the disease. This delay in diagnostic evaluation leads to a delay in treatment. Delays in diagnosis and treatment eventually result in an increase in the mortality rate. Early detection will not only reduce mortality but will also improve quality of life after treatment.
Who is advised to get an early screening?
Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer. As a result, those who smoke or used to smoke but do not currently exhibit any symptoms of lung cancer are at an increased risk of developing the disease. Therefore, early lung cancer screening is recommended for people who smoke or used to smoke, who have been exposed to secondhand smoke or radon gas, and those who have inhaled particulate matter( pollution, asbestos, etc.) for a long period of time in their lives.
How is Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Any abnormal growth of cells or the presence of tumours can be found in medical studies, which include:
- Medical history and physical exam
In order to learn about symptoms and potential risk factors, the doctor will enquire about the patient’s medical history. Additional tests, such as imaging and biopsies, may be carried out to ascertain whether lung cancer is present if the physical examination raises any concerns.
- Chest x-ray
As a first step in ruling out lung cancer, doctors use these tests. An X-ray will show any tumour as a grey-white mass, and it is difficult to determine if it is cancerous or not. More tests might be ordered by the doctor if anything unusual is found.
- Low dose CT Scans (LDCT)
A procedure that creates a series of precise images of various locations inside the body using a computer connected to an x-ray equipment that emits a very low dose of radiation. The images, which are obtained from various angles, are then used to provide 3-D depictions of the tissues and organs.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
In a CT scan, X-rays are used to do detailed imaging. A CT scan can quickly identify a lung tumour and also reveal its shape, size, and location. A CT scan can also show whether lung cancer has spread elsewhere.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
MRI uses radio waves and string magnets rather than X-rays to produce detailed images of the body’s soft tissues.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
FDG, a type of radioactive sugar, is injected into the circulation and is taken up by the cells. More sugar tends to be absorbed by cancerous cells than by healthy cells. This helps in separating tumours from healthy cells.
- PET/CT scan
The doctor obtains a comprehensive image of the sites with increased radioactivity using a PET scan and a CT scan. This type of scan is able to evaluate how far cancer has spread and how successfully the current course of treatment is working.
- Needle biopsy
A hollow needle is inserted in a suspicious area to get a small sample of the tissue, which is then studied under a microscope for the presence of tumours. Biopsies don’t involve any surgical incisions and are minimally invasive.
Cancer can result in the loss of health, confidence, time, and money for an individual. In advanced stages of cancer, life becomes very unpredictable. One might lose the courage to fight the battle over time. But early detection can increase the chances of victory against cancer. One can preserve their good health while eradicating cancer with minimal treatment approaches. Early detection will enhance the quality of life after treatment. Therefore, it is recommended to get screened for cancer within a span of 2 years.
References:
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- https://www.webmd.com/lung-cancer/lung-cancer-what-causes
- https://moffitt.org/cancers/lung-cancer/faqs/what-is-the-difference-between-small-cell-lung-cancer-non-small-cell-lung-cancer/
- https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/lung-cancer/stages
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/lung-cancer/lung-cancer-treatmen
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/detection.html